Search for your domain name
.COM Domain Name Only $11.99
Register your domain with us and enjoy:
Everything you need to get online – FREE with your domain.
Each and every POWERHOSTER.COM domain name comes with all you need to get online.
Domain Forwarding and Masking
Direct any domain name you own to your website — anyone who types that domain name into their browser is taken directly to your website.
Domain Locking
Domain locking prevents accidental or intentional transfers of domain ownership and stops anyone from redirecting your nameservers.
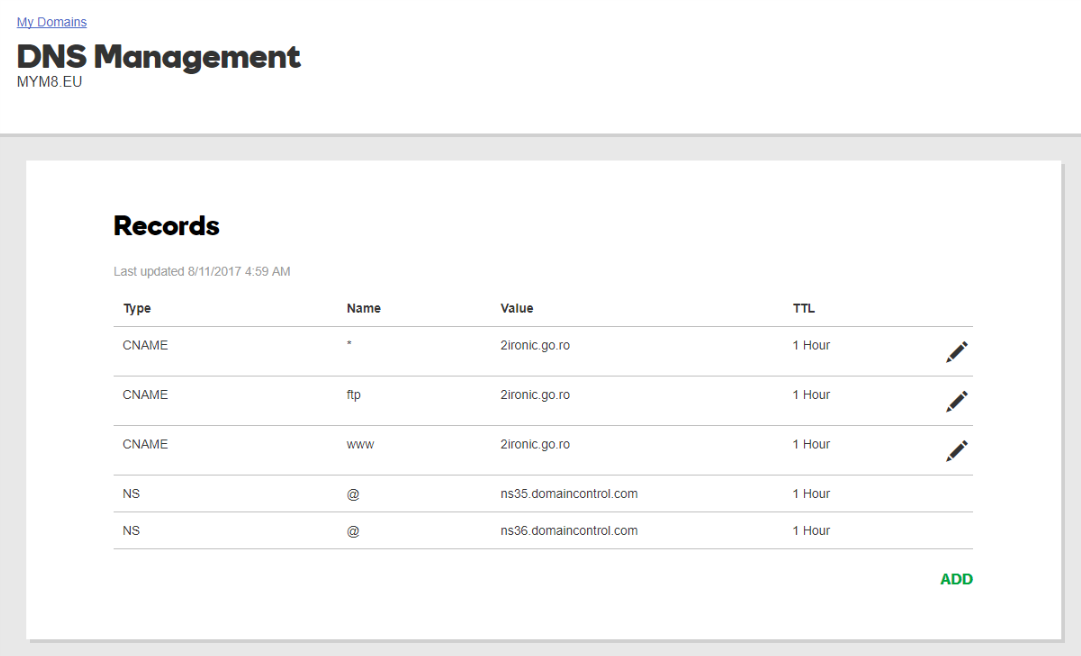
Total DNS Control
Manage your domain nameserver (DNS) records and set your email, FTP, sub-domains and website location — all from one control panel.
Change of Registration
Assign your domain name to someone else or change the contacts for your domain online anytime. Requires a fee for domains.
Status Alerts
Monitor the status of your domain and get instant alerts if there’s been a change.
Auto Renew Protection
No need to watch expiration dates to make sure you renew on time! Auto renew keeps your domains, hosting, website builders, and other products in your name and under your control.
|
Private Registration
Keeps your personal information private, protecting you from spam, scams and worse.
|
|
|
Internationalized Domain Names (IDN)
Register .COM, .NET, .ORG and other popular domain names in any one of over 100 native languages, ranging from Afrikaans to Vietnamese. Search using English or native character sets.
|
|
|
Domain Transfers
Transfer your domains to POWERHOSTER.COM – it’s fast, automated and risk-free! You keep all the time remaining on your registration and get a 1-year extension at no extra charge.
|
|
|
Domain Backorders
Watch the status of any domain currently registered to someone else. Secure your chance to register that domain when it becomes available by backordering it at special savings.
|
|
|
Bulk domain discounts
SAVE up to 93% when you register or transfer six or more .COMs at once.***
|
What is a domain name?
A domain name, like www.powerhoster.com, is a lot like a street address for a house or business. Let’s use the White House as an example. The street address, 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue, is an exact location — like an IP address. You might not know the exact street address, but when you visit Washington, D.C., you can tell your cabbie that you want to visit the White House and still get there. This is how a domain name is used: It’s an easy way to reach the exact location of a website without having to remember its numeric address.
A domain name consists of, at least, a top-level and a second-level domain. A top-level domain (TLD) is the part of the domain name located to the right of the dot (“.”). The most common TLDs are .com, .net, and .org.
Many domains, also called extensions, can be registered by anyone, like .com, .net, and .org. A second-level domain (SLD) is the portion of the domain name that is located immediately to the left of the dot and domain name extension. For example, the SLD in coolexample.com is coolexample.
Advanced Domain Name Description: A domain name represents a physical point on the Internet — an IP address. The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) governs coordination of the links between IP addresses and domain names across the Internet. With this standardized coordination, you can find websites on the Internet by entering domain names instead of IP addresses into your Web browser.
What is an IP Address?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifying string of numbers, like 216.27.61.137, given to every individual computer, server, and network on the Internet. Like a license plate is used to help identify vehicles, an IP address is used to identify and locate information online. Additionally, they allow for communication over the internet between devices and networks connected to the internet.
HOW DOES Domain Name WORK?
When setting up a website, you purchase a domain name and a hosting account (a web server to house the website). These items can be purchased from two separate businesses or from the same. It is usually more cost-effective to purchase them separately. You may find that, although most hosting companies offer low-cost hosting, a cheaper price for a domain name can be found at companies who specialize in registering domain names.
The same can be said for companies offering low-cost domain name registration; their hosting packages almost doubles the lowest packages offered elsewhere. After purchasing both elements (domain name and hosting account), the domain name needs to be pointing to (or referencing) the location of the hosting account. To do this, the Domain Name Servers need to be configured to the web servers of the hosting account. After all of this is done, the DNS will be able to point any browsers to the correct IP address of the website once the domain name is typed into the browser. For more information, please check this link
What is the ‘www’ before my domain name?
The www before your domain name is a subdomain, not part of the domain name itself. Therefore, if you set up your www CNAME record to point to your primary A record, your site will resolve both at www.coolexample.com and coolexample.com.
If you can reach your website by typing in your domain without the www but cannot reach it when you type the www, then your CNAME might be set up incorrectly. Follow the instructions below to ensure your domain name’s settings are correct.
What is a nameserver?
Nameservers are the Internet’s equivalent to phone books. A nameserver maintains a directory of domain names that match certain IP addresses (computers). The information from all the nameservers across the Internet is gathered in a central registry.
Nameservers make it possible for visitors to access your website using a familiar domain name, instead of having to remember a series of numbers.
What do I do with my domain once it’s been registered?
Registering a domain name does not automatically activate a website that displays when visitors enter your domain name into a Web browser. The domain name must have a hosted website that includes a numeric address, called an IP address, for visitors to access the website using your domain name.
Besides setting up a website, there are a number of things you can do with your domain name once you register it.
- Sell it — Domain names can be a great investment. If you have registered a domain name that you are not using, maybe someone else can. You can set up a For Sale parked page to let visitors know that it’s available — and don’t forget to include your contact information. See Auctions FAQ for more information.
- Protect your brand online — The more domain names you register, the better. Prevent others from registering a similar domain name to yours. These similar domain names can steal your customers or confuse them. What can you do with all these domain names? Forward them to your main domain name’s website. See Manually forward or mask your domain or subdomain for more information.
- Hold on to it — Maybe you haven’t decided what to do with your new domain name. Don’t worry — there’s no rush. You can leave it parked with us for the length of your registration.
Why should I register more than one domain name?
If you’re thinking about registering more than one domain name, you’ve got the right idea. Registering and using multiple domains names is great for building your business, protecting your brand name, and creating a dynamic online identity.
When you register multiple domain names, you can:
- Keep your competition from registering a similar domain name drawing customers to them instead of you
- Promote the different products and services you offer
- Drive more traffic to your website
- Enjoy more opportunities to market to — and be listed in — search engines
- Create distinct advertising strategies reaching different target markets
- Provide customers more ways to find you when searching the Internet
- Capture common misspellings of your domain name, instead of sending visitors to an error page
- Protect your brand and online identity
When can I register an expired domain name?
Usually, a domain name is not available for re-registration as soon as it expires. Most registrars allow a grace period that can be as short as one or two weeks or as long as a year for registrants to renew expired domain names. The actual grace period can be different for each individual registrar and domain name extension. That is, the grace period for a .com domain name might be different from the grace period for a .us domain name, even at the same registrar.
After the registrar’s grace period, most domain names have a redemption period. This period can last from two weeks to 30 days, and, during this time, the current registrant can renew the domain name by paying a redemption fee along with the domain name’s renewal fee.
If the current registrant does not renew or redeem the domain name, it might be auctioned. When a domain name is released to a public auction, you can participate and possibly capture the domain name by placing a bid on it.
If the domain name is not renewed, redeemed, or purchased through an auction, it is returned to its registry. The registry determines when the domain name is released again for registration. Once it’s released, you can register the domain name through us.
Note: A registrant can renew an expired domain name at no extra cost up to day 18. If they renew an expired domain name anytime between day 19 and day 30, they must also pay an $80.00 redemption fee. The domain name may not be renewed if there is a buyer in auction after day 30.
Can a domain name registered elsewhere use your system to register new nameservers?
No, you must register your domain name through us to use our system to register nameservers for it. For domain names registered elsewhere, you must register nameservers through your current registrar.
For more information, contact your current registrar.
If you registered nameservers through our system, you can assign them to domain names registered elsewhere.
Who is listed as a domain name’s registrant?
A public domain name registration with us lists registrant and other domain name contact information on the Whois database exactly as it appears in your account with us. This listing is standard procedure for all registrars certified by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). You can change the domain name contact information if you want.
To restrict your personal information from displaying in a Whois database listing, you can purchase domain name privacy.
What is the Uniform Domain Name Dispute Resolution Policy?
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) has a Uniform Domain Name Dispute Resolution Policy (UDRP) which defines how to resolve trademark-based disputes over domain names. In accordance with the UDRP, you can dispute a claim to a domain name by following ICANN’s Uniform Domain Name Disputes Resolution Policy.
Note: The UDRP does not apply to country-code top-level domains names (ccTLDs), except in a few cases where the local administrator has decided to adopt it.
Can I register domain names if I don’t have a hosting provider?
Yes. You can register domain names before you find a hosting provider, and, in fact, you are not required to host a domain name.
When you register a domain name with us, we automatically park it. A temporary, parked page displays when visitors type the domain name into their browser’s address bar. The parked page indicates you are reserving the site.
All the TLDs we can Register
A top-level domain name (TLD) is the last part of a domain name. For example, in coolexample.com, the TLD is the .com.
A gTLD is a generic top-level domain name. These are not linked to geographical regions or special authorities. gTLDs are typically used to describe organizations and businesses.
A
- .aero — Aviation Community members only
- .asia — Companies and individuals based in the Asia-Pacific region
B
- .biz — Intended for business use
C-G
- .com — Considered commercial and is the most widely used TLD on the Internet
- .coop — Reserved for cooperative businesses
- .edu — Available to higher learning educational institutions that grant degrees
- .gov — Reserved for U.S. government agencies
H-M
- .info — Used for informational purposes
- .jobs — Used for employment and job-related websites
- .mil — Reserved for use by the U.S. Military
- .mobi — Dedicated to sites that are made for mobile device use
- .museum — Reserved for museums
N-R
- .name — For individual use generally using a first and last name
- .net — Usually used by Network Providers, but used widely by businesses and individuals for other purposes
- .org — Commonly used by non profit organizations
- .pro — Used for specific professions, usually intended for licensed professions. Examples include: Attorneys, Doctors etc.
S-Z
- .sch — Reserved for schools
- .tel — Internet Communication Services
- .travel — Reserved for the travel and tourist industry and must be verified as a legitimate travel-related entity
Open TLD
Open TLDs are top-level domain names that are open to the general public for registration.
A-G
- .biz — Intended for business use
- .com — Intended for Commercial use and the most popular domain name extension on the Internet.
H-M
- .mobi — Dedicated to sites that are made for mobile device use
N-R
- .name — For individual use, generally using a first and last name
- .net — Usually used by network providers, but used widely by businesses and individuals for other purposes
- .org — Commonly used by non-profit organizations
S-Z
All the ccTLDs We can Register
ccTLDs are country-code top-level domain names. They are two letters long instead of three and are active sometimes even if the country the ccTLD was created to represent no longer exists.
A
- .ac — Ascension Island
- .ad — Andorra
- .ae — United Arab Emirates
- .af — Afghanistan
- .ag — Antigua and Barbuda
- .ai — Anguilla
- .am — Armenia
- .an — Antigua and Barbuda
- .ao — Angola
- .aq — Antarctica
- .ar — Argentina
- .as — American Samoa
- .at — Austria
- .au —Australia
- .aw — Aruba
- .az — Azerbaijan
B
- .ba — Bosnia and Herzegovina
- .bb — Barbados
- .bd — Bangladesh
- .be — Belgium
- .bf — Burkina Faso
- .bg — Bulgaria
- .bh — Bahrain
- .bi — Burundi
- .bj — Benin
- .bm — Bermuda
- .bn — Brunei Darussalalm
- .bo — Bolivia
- .br — Brazil
- .bs — Bahamas
- .bt — Bhutan
- .bv — Bouvet Island
- .bw — Botswana
- .by — Belarus
- .bz — Belize
C-D
- .ca — Canada
- .cc — Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- .cd — Democratic Republic of the Congo
- .cf — Central African Republic
- .cg — Republic of the Congo
- .ch — Republic of Switzerland
- .ci — Cote dlvoire
- .ck — Cook Islands
- .cl — Chile
- .cm — Cameroon
- .cn — China, mainland
- .co — Colombia
- .cr — Costa Rica
- .cu — Cuba
- .cv — Cape Verde
- .cx — Christmas Island
- .cy — Cyprus
- .cz — Czech Republic
- .de — Federal Republic of Germany
- .dj — Djibouti
- .dk — Denmark
- .dm — Dominica
- .do — Dominican Republic
- .dz — Algeria
E-F
- .ec — Ecuador
- .ee — Estonia
- .eg — Egypt
- .er — Eritrea
- .es — Spain
- .et — Ethiopia
- .eu — European Union
- .fi — Finland
- .fj — Fiji
- .fk — Falkland Islands
- .fm — Federated States of Micronesia or radio related websites in general
- .fo — Faroe Islands
- .fr — France
G-H
- .ga — Gabon
- .gb. — United Kingdom, not used as widely as .uk
- .gd — Grenada
- .ge — Georgia
- .gf — French Guiana
- .gg — Guernsey
- .gh — Ghana
- .gi — Gibraltar
- .gl — Greenland
- .gm — Gambia
- .gn — Guinea
- .gp — Guadeloupe
- .gq — Equatorial Guinea
- .gr — Greece
- .gs — South Sandwich Islands and South Georgia
- .gt — Guatemala
- .gw — Guinea-Bissau
- .gy — Gyana
- .hk — Hong Kong
- .hm — Heard Island and McDonald Islands
- .hn — Honduras
- .hr — Croatia
- .ht — Haiti
- .hu — Hungary
I-J
- .id — Indonesia
- .ie — Ireland
- .il — Israel
- .im — Isle of Man
- .in — India
- .io — British Indian Ocean Territory
- .iq — Iraq
- .ir — Iran
- .is — Iceland
- .it — Italy
- .je — Jersey
- .jm — Jamaica
- .jo — Jordan
- .jp — Japan
K-L
- .ke — Kenya
- .kg — Kyrgyzstan
- .kh — Cambodia
- .ki — Kiribati
- .km — Comoros
- .kn — Saint Kitts and News
- .kp — North Korea
- .kr — South Korea
- .kw — Kuwait
- .ky — Cayman Islands
- .kz — Kazakhstan
- .la — Laos
- .lb — Lebanon
- .lc — Saint Lucia
- .li — Liechtenstein
- .lk — Sri Lanka
- .lr — Liberia
- .ls — Lesotho
- .lt — Lithuania
- .lu — Luxembourg
- .lv — Latvia or popularly known as “Las Vegas”
- .ly — Libya
M
- .ma — Morocco
- .mc — Monaco
- .md — Moldova
- .me — Montenegro and also a domain name for personal websites
- .mg — Madagascar
- .mh — Marshall Islands
- .mk — Republic of Macedonia
- .ml — Mali
- .mm — Myanmar
- .mn — Mongolia
- .mo — Macau
- .mp — Northern Mariana Islands
- .mq — Martinique
- .mr — Mauritania
- .mt — Malta
- .mu — Mauritius
- .mv — Maldives
- .mw — Malawi
- .mx — Mexico
- .my — Malaysia
- .mz — Mozambique
N
- .na — Namibia
- .nc — New Caledonia
- .ne — Niger
- .nf — Norfolk Island
- .ng — Nigeria
- .ni — Nicaragua
- .nl — Netherlands
- .no — Norway
- .np — Nepal
- .nr — Nauru
- .nu — Niue
- .nz — New Zealand
O-P
- .om — Oman
- .pa — Panama
- .pe — Peru
- .pf — French Polynesia
- .pg — Papua New Guinea
- .ph — Philippines
- .pk — Pakistan
- .pl — Poland
- .pm — Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
- .pn — Pitcairn Islands
- .pr — Puerto Rico
- .pt — Portugal
- .pw — Palau
- .py — Paraguay
Q-R
- .qa — Qatar
- .re — Reunion
- .ro — Romania
- .rs — Serbia
- .ru — Russia
- .rw — Rwanda
S-T
- .sa — Saudia Arabia
- .sb — Solomon Islands
- .sc — Seychelles
- .sd — Sudan
- .se — Sweden
- .sg — Singapore
- .sh — Saint Helena
- .si — Slovenia
- .sj — Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands
- .sk — Slovakia
- .sl — Sierra Leone
- .sm — San Marino
- .sn — Senegal
- .so — Somalia
- .sr — Suriname
- .st — Sao Tome and Principe
- .su — The former Soviet Union
- sv — El Salvador
- .sy — Syria
- .sz — Swaziland
- .tc — Turks and Caicos Islands
- .td — Chad
- .tf — French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- .tg — Togo
- .th — Thailand
- .tj — Tajikistan
- .tk — Tokelau
- .tl — East Timor
- .tm — Turkmenistan
- .tn — Tunisia
- .to — Tonga
- .tp — East Timor
- .tr — Turkey
- .tt — Trinidad and Tobago
- .tv — Tuvalu and popularly used for television-related sites
- .tw — Taiwan
- .tz — Tanzania
U-V
- .ua — Ukraine
- .ug — Uganda
- .uk — United Kingdom
- .us — US territories
- .uy — Uruguay
- .uz — Uzbekistan
- .va — Vatican City State
- .vc — Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- .ve — Venezuela
- .vg — British Virgin Islands
- .vu — Vanuatu
W-X
- .wf — Wallis and Futuna
- .ws — Western Samoa and also promoted for general use as “website”
Y-Z
- .ye — Yemen
- .yt — Mayotte
- .yu — Yugoslavia
- .za — South Africa
- .zm — Zambia
- .zw — Zimbabwe